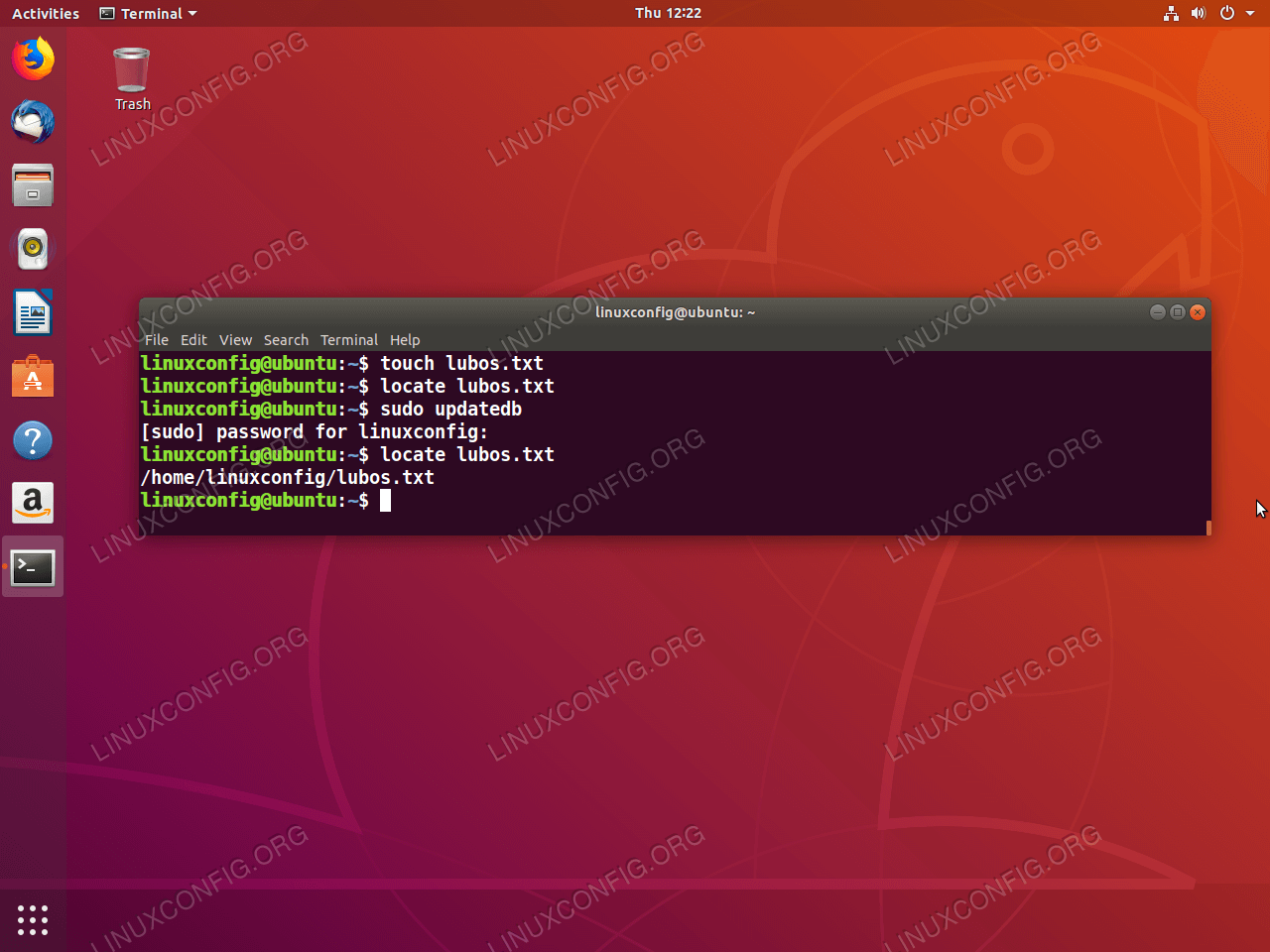
The command CHMOD stands for change mode, and this is used to change the permission of a File or Directory The Command CHOWN stands for Change Owner and this is used to change the ownership of a File or DirectoryClick below button to copy the code By Linux tutorial teamMode refers to symbolic referencing If I want to add executable permission to a file, I enter in chmod x FILE chmod x FILE chmod x FILE And that will add executable permissions We've gone over the basics, we'll fix a folder structure and make it available to us

Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube
How to use chmod command in ubuntu
How to use chmod command in ubuntu-Control who can access files, search directories, and run scripts using the Linux's chmod command This command modifies Linux file permissions, which look complicated at first glance but are actually pretty simple once you know how they work chmod Modifies File PermissionsYou can change file permissions with the chmod command In Unix, file permissions, which establish who may have different types of access to a file, are specified by both access classes and access types Access classes are groups of users, and each may be assigned specific access types
/mkdir-linux-5c4763ffc9e77c00014ae996.png)


How To Create Directories In Linux With The Mkdir Command
In this process, we have to work as under Make a copy of any normal command file in the directory /usr/bin/ as a different name cp /usr/bin/ls /usr/bin/bwc Copy the content of " chmod " file into the newly created file " bwc " cat /usr/bin/chmod > /usr/bin/bwc This will replace the content ofWhat happens if i run the command sudo chmod R 776 in ubuntu Plz help and it has cause ny pc for a black screen errorChmod is very useful tool to manage file modes like read write execute One of the most used option for chmod is x which stands for execution rights In this tutorial we will look different use cases for user or owner, group and others roles List Current User and Group Of A File
The chmod command modifies the permission mode of objects in the system It is one of the most used and important commands in the set of Linux security commands A plus () symbol adds a permission, and a minus () symbol removes a permission You can read chmod ur as "user plus read," as it gives the user read permissionMost of the fresh users to Linux are searching for a way via the command prompt to modify the file/directory permissions Those users would be pleased to knowChmod stands for change mode, which changes the file or directory mode bits To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions Following is a sample of ls l command output In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of users Three file permissions read permitted to read the contents of file
The chmod command allows a user to grant or revoke the read, write, and execute using various methods like numeric mode, symbolic, or reference file Syntax To change permission is the only right of the root user and owner of the file to change the permission of root user fileGroup can read, write and executeIf you need to change a file permission, use the chmod command It also allows to change the file permission recursively to configure multiple files and subdirectories using a single command In this tutorial, you will learn how to use chmod recursively and change file permission on Linux


Q Tbn And9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau



Ubuntu Webdav Client 3 Quick Guides For Easy Setup
Also, some other tasks that we can do with the chmod command Basic Syntax of chmod Recursive Command The basic syntax of changing file/directories permission recursively using chmod is given below chmod R Mode File Where R This option is used to change permissions recursivelyThe chmod command can modify the read, write, and execute tasks with just a root password on a Linux system In the entire post, we will discuss the differences between the chmod 777, chmod 755, or chmod 600, and more other chmod commands on the Linux systemUsing chmod command is very easy if you know what permissions you have to set on a file For example, if you want the owner to have all the permissions and no permissions for the group and public, you need to set the permission 700 in absolute mode chmod 700 filename You can do the same in symbolic mode



Basic Ubuntu Commands Every Beginner Should Know



How To Set Chmod 777 To A Folder And All Its Contents Dev Community
The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty ImagesLinux chmod command is one of the most commonly used commands especially by system administrators when assigning modifying file and folder permissions It's usually used when installing and configuring various services and features in a Linux systemAs you may know, the chmod (stands for Ch ange mod e) command is used to set or change the access permissions of a file or directory in Unixlike systems So if the executable permission of chmod is removed, you can't assign the permissions to any programs, including the chmod command itself



How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples



Bind Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
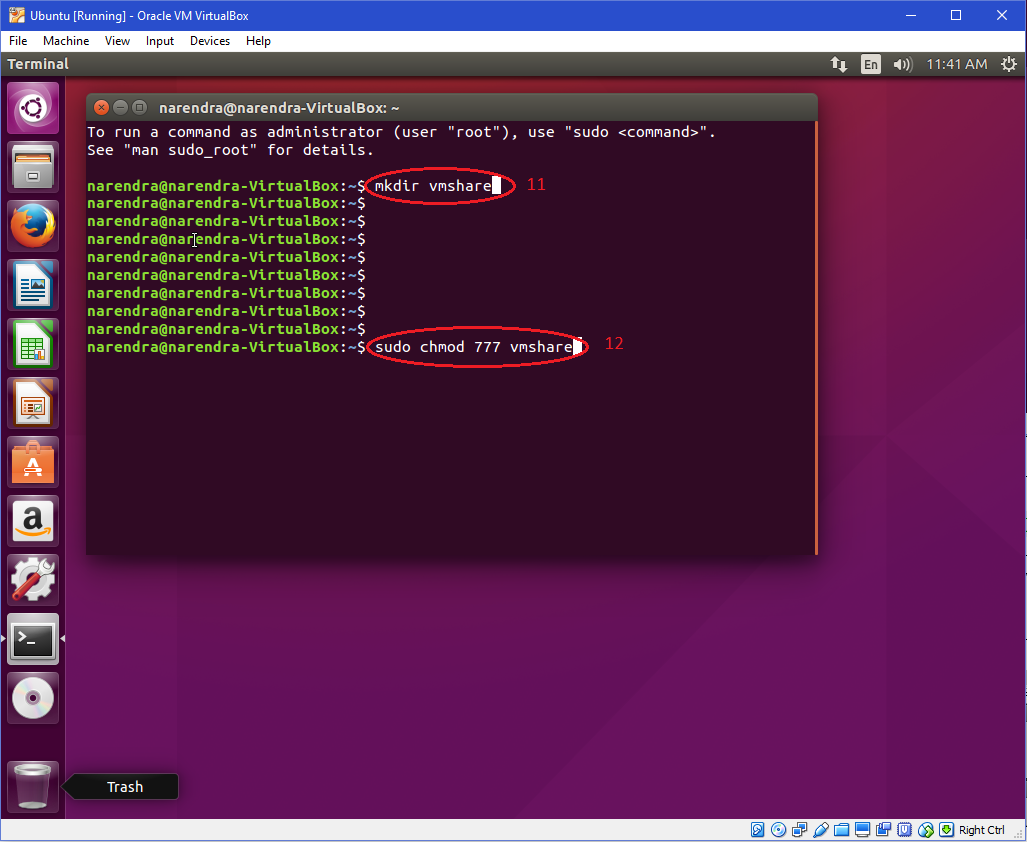
Through the chmod command, you can grant permission to all users using several method references, numeric, symbolic In the reference method, you need to reference a particular file to have the same permissions set In the case of numeric you have to assign numeric value each number get to sum up like for read (4) write (2) execute (1)Chmod is an easy command in Linux However, it becomes difficult when you use all of its variations This command executes in so many ways Nevertheless, you need to know about file permissionsRoot's crontab e has the lines @reboot mkdir p /tmp/vimbackups @reboot chmod 777 /tmp/vimbackups @reboot anotherCommand After boot, the directory has been made, but it still has the default 755 permissions (The dir is forvimrc's set backupdir=/tmp/vimbackups, if that matters)



Issue With Installing Stard Issue 14 Jeryia Stard Github



Give Permissions In Ubuntu Itechzo Give Permissions In Ubuntu
$ chmod ox appsh Change File Mode For All In some cases we can see the x without a definition This is used for all which is equivalent for user , group and others Alternative is adding a like below $ chmod ax appsh OR $ chmod x appshChmod is Linux command used to change file permissions chmod changes user, group and other read, write and execute permission chmod 755 is popular use case for chmod chmod 755 is generally used to make most of the operations without problem because it provides ease for system administrators while running applications chmod 755What happens if i run the command sudo chmod R 776 in ubuntu Plz help and it has cause ny pc for a black screen error



Running Vivado On Linux Ubuntu



How To Install Enve On Ubuntu 2d Animation Software For Linux Connectwww Com
Linux Solution 1 chmod R 755 will set this as permissions to all files and folders in the tree You can use the find commandIn Unixlike operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file The name is an abbreviation of change modeWe can present permissions as an octal number For example, for setting read, write & execute permissions for the owner, read & write permissions for its group, and no permission for others, to a hellotxt file, we will execute the following command sudo chmod u =rwe, g =rw,orwx hellotxt


Linux Commands Linuxconfig Org



Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode
This video covers the chmod command in depth and everything you want to know about change modeBoth Octal and symbolic modesUsing "Chmod x" Command on Linux and Unix with Examples In Linux systems, " chmod " command is used to determine the access rights of users to files It allows us to change the access permissions of the files we specify The exact equivalent of chmod is change mode When we examine the example below;You can change file permissions in this format chmod options mode file_name You can change permissions using alphanumeric characters (arwx) or with octal numbers (777) Here's a chmod example using for setting permissions so that Owner can read, write and execute;



Linux Permissions Posix Chmod Chown Chgrp Youtube



Install Http 2 Lamp Stack On Ubuntu 18 04 Server Linux Apache Mysql Php
Also, some other tasks that we can do with the chmod command Basic Syntax of chmod Recursive Command The basic syntax of changing file/directories permission recursively using chmod is given below chmod R Mode File Where R This option is used to change permissions recursivelyIn this article, we would discuss how to set permissions on files & directories using chmod in Ubuntu distribution chmod is a commandline utility, which is used to change file mode bits But, first we need to discuss a bit about file & directory permissions itself We can long list the contents of a file & directory using ls command with l optionMost of the fresh users to Linux are searching for a way via the command prompt to modify the file/directory permissions Those users would be pleased to know


Windows Faq



How To Create A Custom Ubuntu Distribution With Distroshare Ubuntu Imager
Chmod is a Linux command that will let you \"set permissions\" (aka, assign who can read/write/execute) on a fileUsing "Chmod x" Command on Linux and Unix with Examples In Linux systems, " chmod " command is used to determine the access rights of users to files It allows us to change the access permissions of the files we specify The exact equivalent of chmod is change modeThis video covers the chmod command in depth and everything you want to know about change modeBoth Octal and symbolic modes



Ubuntu Commands A Categorized Cheat Sheet With Examples



Chmod Chown Howto On Debian Ubuntu With Cheatsheet Youtube
Chmod command in Linux is used to change or assign permissions on files and directories In Linux / Unix systems, accessibility to files and directories is determined by file ownership and permissions In a previous article, we looked at how to manage file & directory ownership using the chown commandChmod clears the setgroupID bit of a regular file if the file's group ID does not match the user's effective group ID or one of the user's supplementary group IDs, unless the user has appropriate privileges Additional restrictions may cause the setuserID and setgroupID bits of MODE or RFILE to be ignoredHow to Use the chmod Command on Ubuntu 1604 1804 with Examples About chmod command It changes the mode of each FILE to MODE Syntax The syntax is the rule and format of how the chmod command can be used the systax options can be reordered Options FILE MODE, OCTALMODE c,



How To Use Sleep Command In Linux Ubuntu 19 10 18 04 Lts


1
Most of the fresh users to Linux are searching for a way via the command prompt to modify the file/directory permissions Those users would be pleased to knowMost of the fresh users to Linux are searching for a way via the command prompt to modify the file/directory permissions Those users would be pleased to knowOn a particular directory if you have multiple subdirectories and files, the following command will assign execute permission only to all the subdirectories in the current directory (not the files in the current directory) $ chmod uX *



Bash Sudo Abc Sh Command Not Found Ask Ubuntu



How To Install Tensorflow 2 0 On Ubuntu Pyimagesearch
Chmod ux scriptsh As you'd have guessed, 'ux' says grant () the owner/current user (u) execute (x) access to the file Similarly, for group, you can use 'g' and for others you can use 'o' Please note that whenever you want to grant/revoke a common set of permissions to/from all, you can use 'a' instead of 'ugo'In this article, we would discuss how to set permissions on files & directories using chmod in Ubuntu distribution chmod is a commandline utility, which is used to change file mode bits But, first we need to discuss a bit about file & directory permissions itselfUsing Chmod Command to Change File Permissions As all Linux users, you will at some point need to modify the permission settings of a file/directory The command that executes such tasks is the chmod command The basic syntax is



Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube



Windows Subsystem For Linux Error 13 Permission Denied While Accessing Directory In Wsl Ask Ubuntu
Mode refers to symbolic referencing If I want to add executable permission to a file, I enter in chmod x FILE chmod x FILE chmod x FILE And that will add executable permissions We've gone over the basics, we'll fix a folder structure and make it available to usThe chmod command in Linux/Unix is abbreviated as CH ange MOD e Chmod command is useful to change permission for Files and folders in Linux/Unix File/Directory permission is either Read or Write or executable for either user or group or othersThe chmod command modifies the permissions of a file or directory on a Linux system The three numbers after the chmod command represent the permissions assigned to user owner, group owner and others The numbers 755 assign readwriteexecute permissions to the user ower and readexecute permissions to group owner and others



Click To Know How To Disable Enable Pen Drive In Ubuntu



Steps To Install Android Studio In Ubuntu
You can use chmod in the command line to change file or directory permissions on unix or unixlike systems such as linux or BSD How to use chmod?How to set chmod for a folder and all of its subfolders and files in Linux Ubuntu Terminal ?A command line / terminal window ( Ctrl Alt T or Ctrl AltF2) A user account with sudo privileges (optional) A Linux system



Basics Of Using Chown And Chmod Commands Anto Online



How To Set Chmod 777 To A Folder And All Its Contents Dev Community
Below are some examples of how to use the chmod command in symbolic mode Give the members of the group permission to read the file, but not to write and execute itchmod g=r filename Remove the execute permission for all users chmod ax filename Repulsively remove the write permission for otherDescription On Unixlike operating systems, a set of flags associated with each file determines who can access that file, and how they can access it These flags are called file permissions or modes, as in "mode of access" The command name chmod stands for "change mode" It restricts the way a file can be accessedUse the m or –mode option set file mode (as in chmod), not a=rwx – umask The syntax of MODE is the same as with the chmod commandp, –parents Use the p or –parents option to make parent directories as neededv, –verbose Verbose output Print a message for each created directory Z


Ruby On Rails Solutions Jjnweb Com



Useful Terminal Commands For Linux Macos And Ubuntu Skillsugar
Recursive chmod using find, pipemill, and sudo To assign reasonably secure permissions to files and folders/directories, it's common to give files a permission of 644, and directories a 755 permission, since chmod R assigns to both Use sudo, the find command, and a pipemill to chmod as in the following examplesThe chmod command is used to modify the permission types for files and directories It works identically for both files and directories It means same command is used to update the permission types for both files and directories Chmod command accepts arguments in two notations;Chmod stands for " Change Mode " and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system By using this command, we can set the read, write, and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups (Owner, Group and Other) in Linux



Ubuntu Clear Read Only Status Issue Blog By Chang Suk


How To Install Drupal Console On Ubuntu Or Macos Drupaltut
We can sort it as a user, group and other from left to right, which comes in 3 blocks after the first characterChmod 755 Chmod 755 (chmod arwx,gw,ow) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can read, can write and can execute (G)roup can read, can't write and can execute (O)thers can read, can't write and can executeLinux Solution 1 chmod R 755 will set this as permissions to all files and folders in the tree You can use the find command For example To change all the directories to 755 (drwxrxrx) find /opt/lampp/htdocs type d exec chmod 755 {} \;



Unix Linux Ubuntu 16 04 A Chmod Command Not Excuted In Rc Local Automatically Youtube



Introduction To The Ubuntu Command Programmer Sought
What happens if i run the command sudo chmod R 776 in ubuntu Plz help and it has cause ny pc for a black screen errorUse the chown command to change file owner and group information we run the chmod command command to change file access permissions such as read, write, and access This page explains how to use chmod and chown command on Linux or Unixlike systems Understanding file permissions for chmod and chown commandChmod aw file (removes all writing permissions) chmod ox file (sets execute permissions for other (public permissions)) chmod u=rx file (Give the owner rx permissions, not w) chmod gorwx file (Deny rwx permission for group, others) chmod gw file (Give write permission to the group) chmod ax file1 file2 (Give execute permission to everybody) chmod grx,ox file (OK to combine like this with a comma) u = user that owns the file g = group that owns the file o = other (everyone else) a
/mkdir-linux-5c4763ffc9e77c00014ae996.png)


How To Create Directories In Linux With The Mkdir Command



Failing To Install Gclone In Wsl Linux V2 Ubuntu 04 Bashonubuntuonwindows
What happens if i run the command sudo chmod R 776 in ubuntu Plz help and it has cause ny pc for a black screen errorThe chmod also called change mode that is used to change permissions of a given file according to a certain mode The chown command stands for "change owner" is used to change the owner of a given file or folder In this tutorial, we will show you how to use the chown and chmod command through simple examplesBy executing this command, the owner can read, write, and execute the file (rwx) However, group and others are only allowed to read (r–) At this point, you might wonder why we are using a threedigit number (744) after the chmod command The number determines the file permissions



Linux Commands Linuxconfig Org


Install Samba On Ubuntu Linux Hint
Linux chmod command is used to change the access permissions of files and directories It stands for change mode It can not change the permission of symbolic links Even, it ignores the symbolic links come across recursive directory traversalUnderstanding the Syntaxes and the chmod Command on Linux u The u syntax mentions the user who owns the file or the directory g The g syntax mentions the group where the file belongs o The o syntax mentions that the file is owned by all the users a The a syntax mentions that the file is owned by



Installing Jira On Ubuntu Server It From Valdemar



Basic Linux Commands Ubuntu



Permission Denied Inside Var Www Html When Creating A Website And It S Files With The Apache2 Server Stack Overflow



Installing Bitwarden On Ubuntu Server It From Valdemar
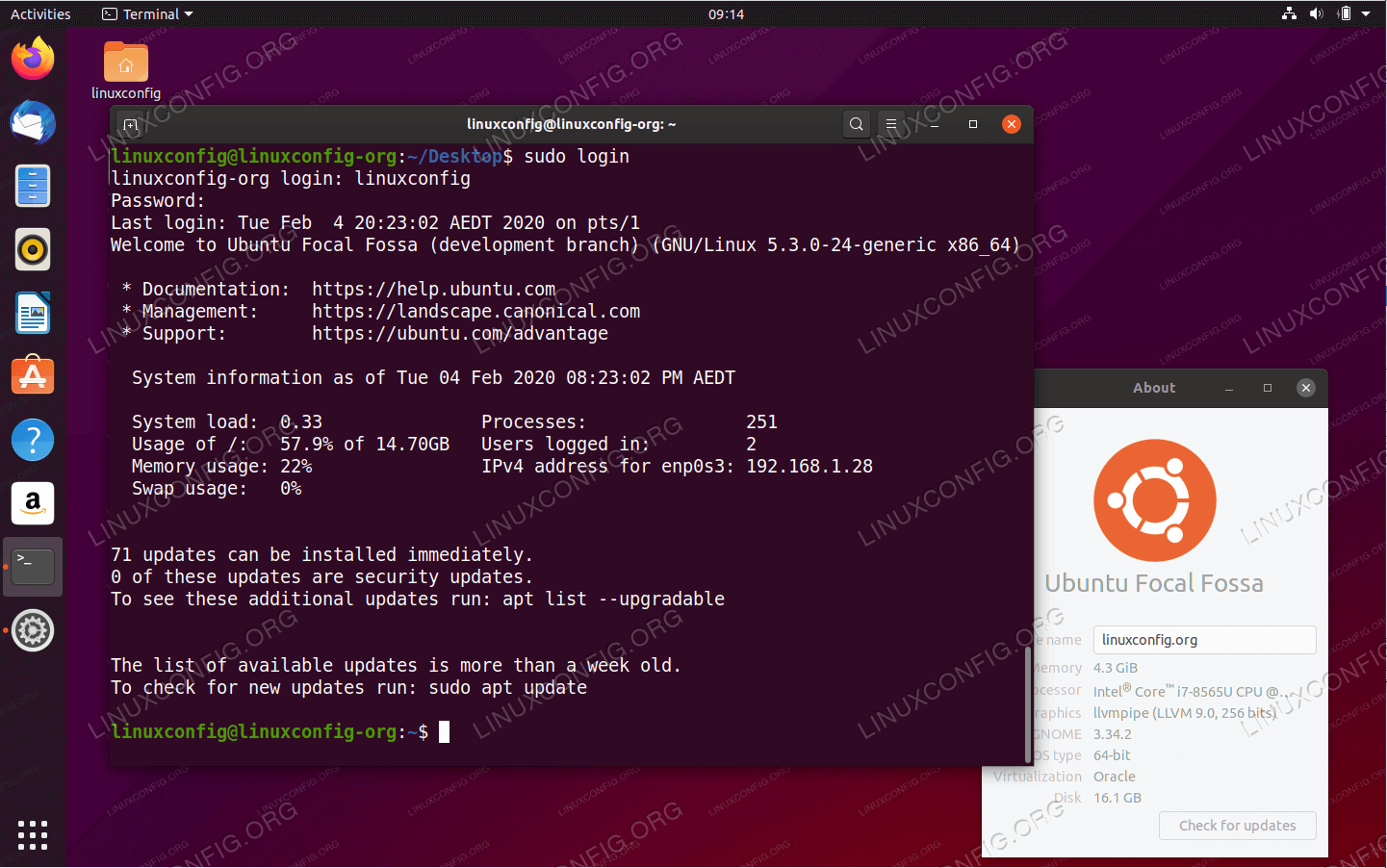


Disable Dynamic Motd And News On Ubuntu 04 Focal Fossa Linux Linuxconfig Org



Pazeidimas Diskriminacinis Riaumoti Ubuntu Wc Yenanchen Com



Install Bolt Cms On Ubuntu 18 04 With Nginx Google Cloud
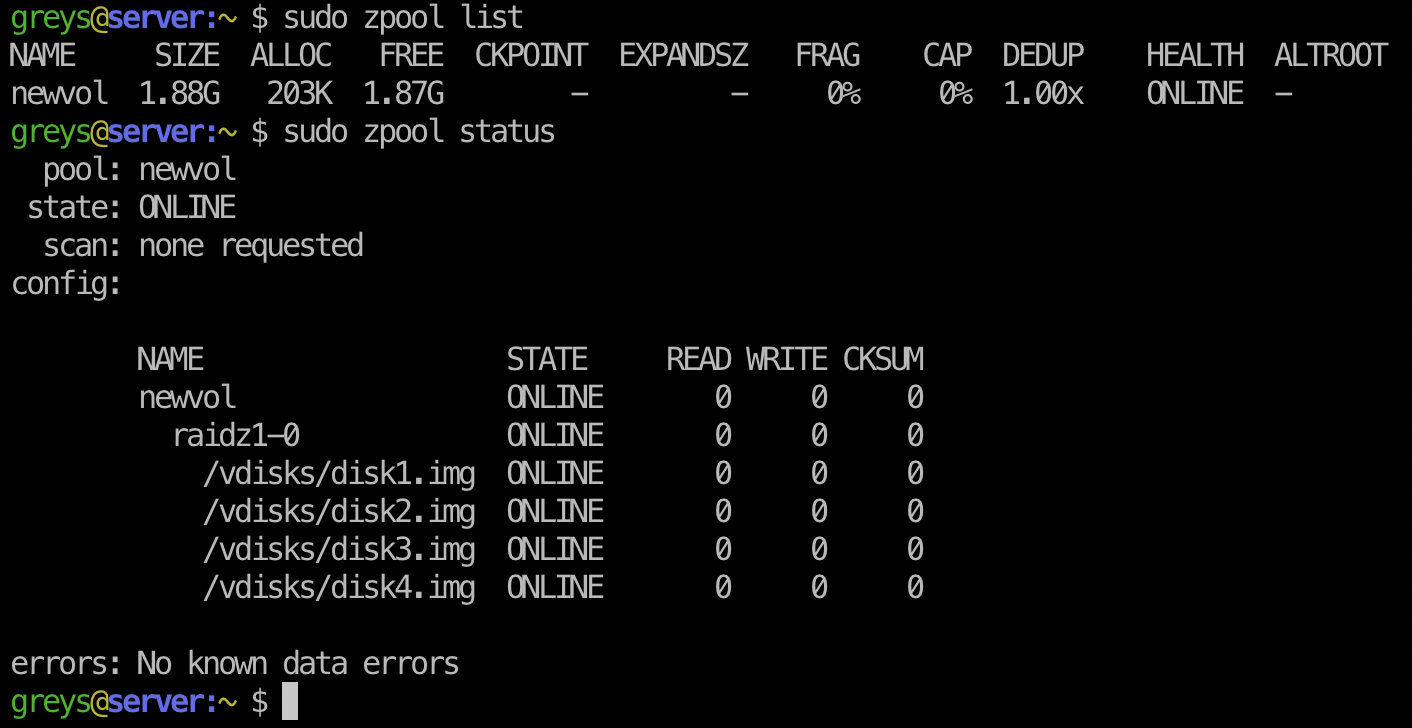


Getting Started With Zfs In Ubuntu 04
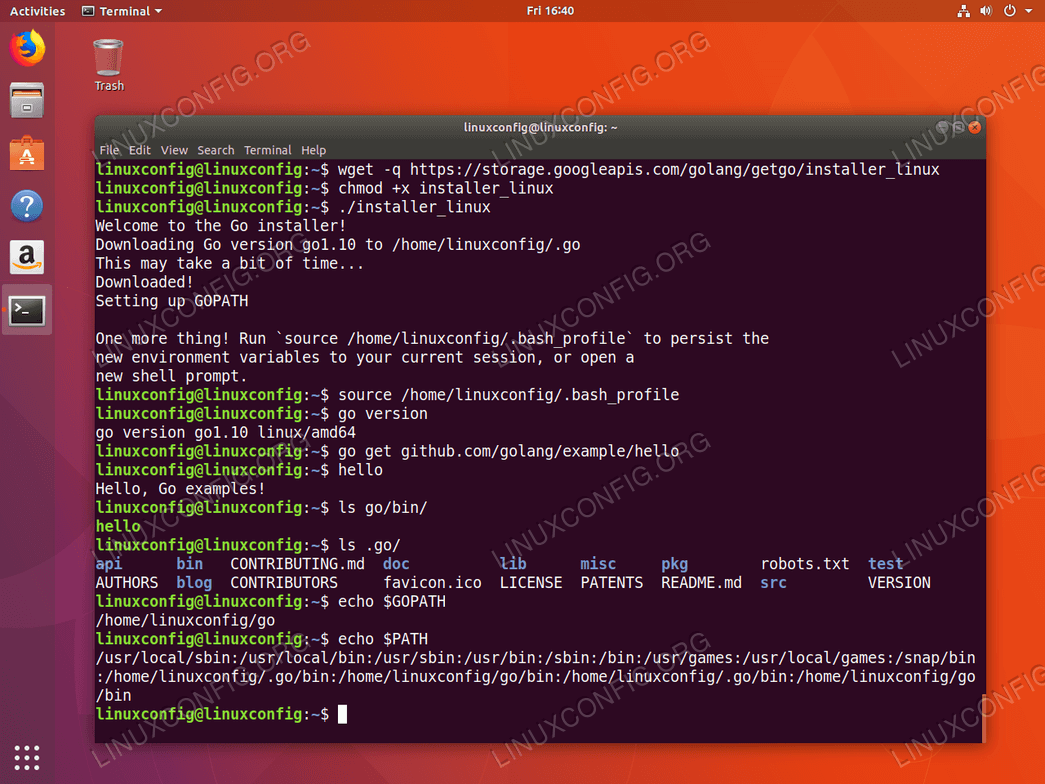


Install Go On Ubuntu 18 04 Bionic Beaver Linux Linuxconfig Org


Q Tbn And9gcs9h1s9aymhgxuiwaruv5svj Iw49oju6dx0zyl3syy0y4ft3ya Usqp Cau



Permissions How To Refresh Privileges On A Script Ask Ubuntu



Command Line Desktop File Fails To Run Ask Ubuntu



Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube



Permissions Not Able To Access Folder Due To Wrong Chmod Commands Ask Ubuntu



Top 50 Linux Commands You Must Know Journaldev



How To Give 777 Permission In All Subfolders In Htdocs Or Any Folder Ubuntu Youtube



How To Become Root In Ubuntu 10 Steps With Pictures Wikihow
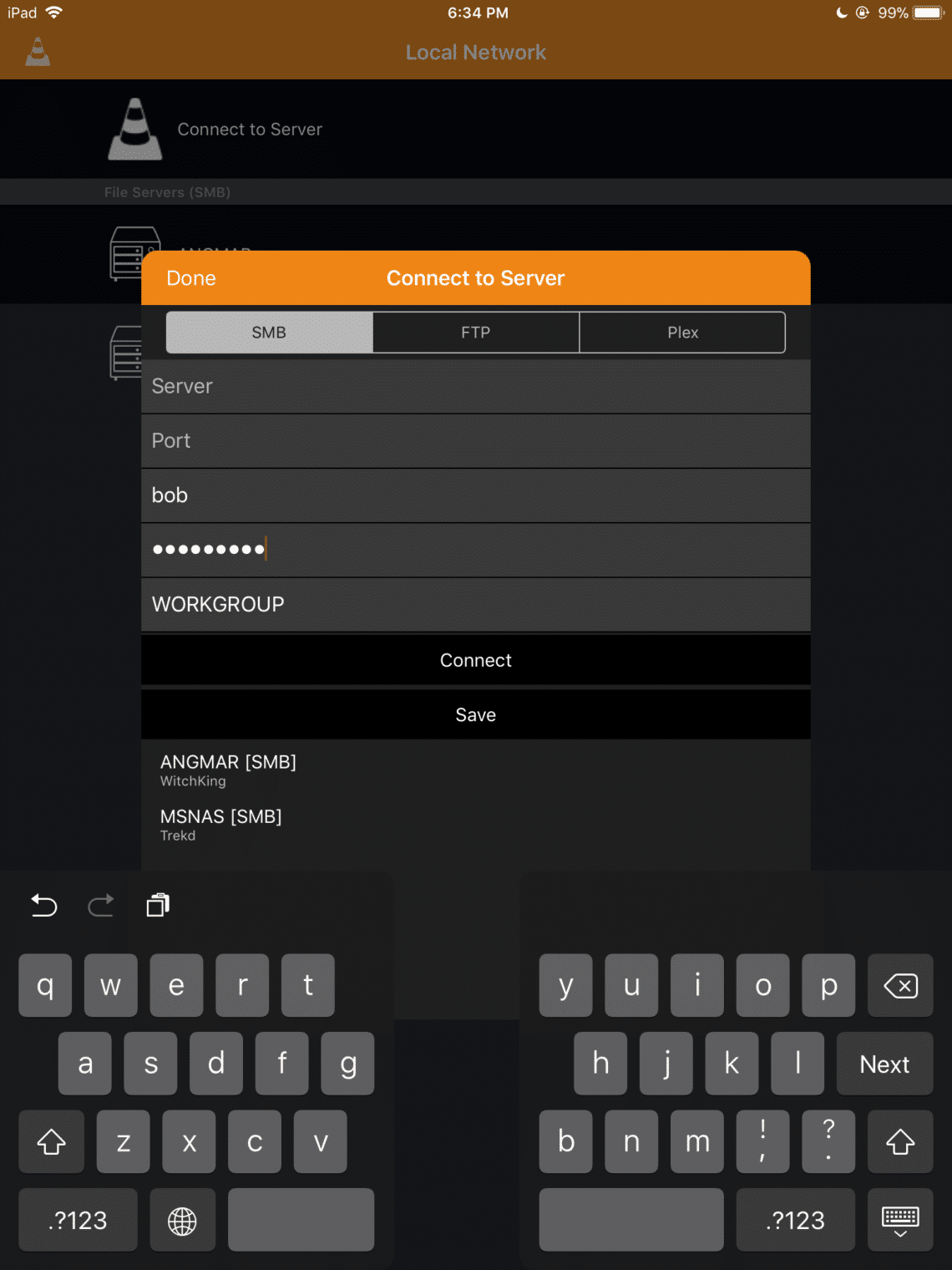


Install Samba On Ubuntu Linux Hint



Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu



Solomondesigns Co Uk How To Install Foundation 6 On An Ubuntu Pc With Sass Compiler Using The Cli
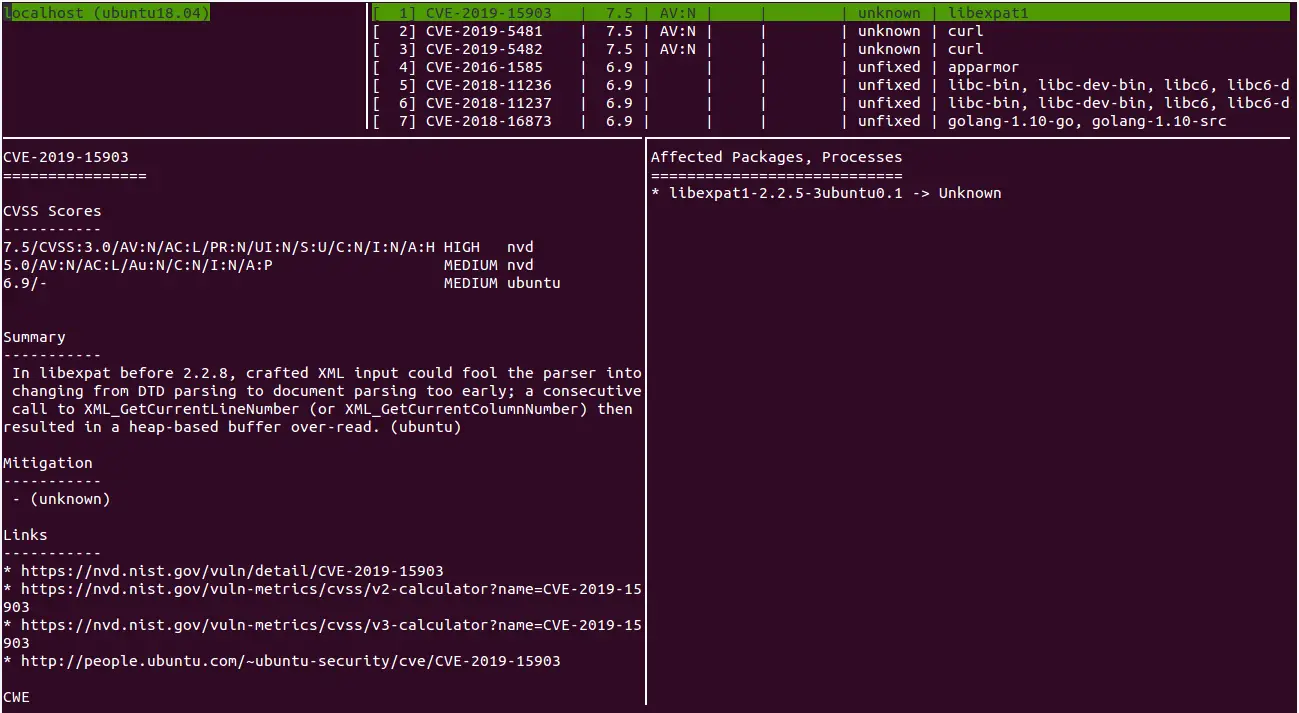


How To Install And Use Vuls Vulnerability Scanner On Ubuntu 18 04 Lts



How To Manage File Permissions On Ubuntu Server 04 Dev Tutorial



Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier



Bash Sudo Abc Sh Command Not Found Ask Ubuntu



How To Install The Losslesscut Video Editor On Linux



Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners
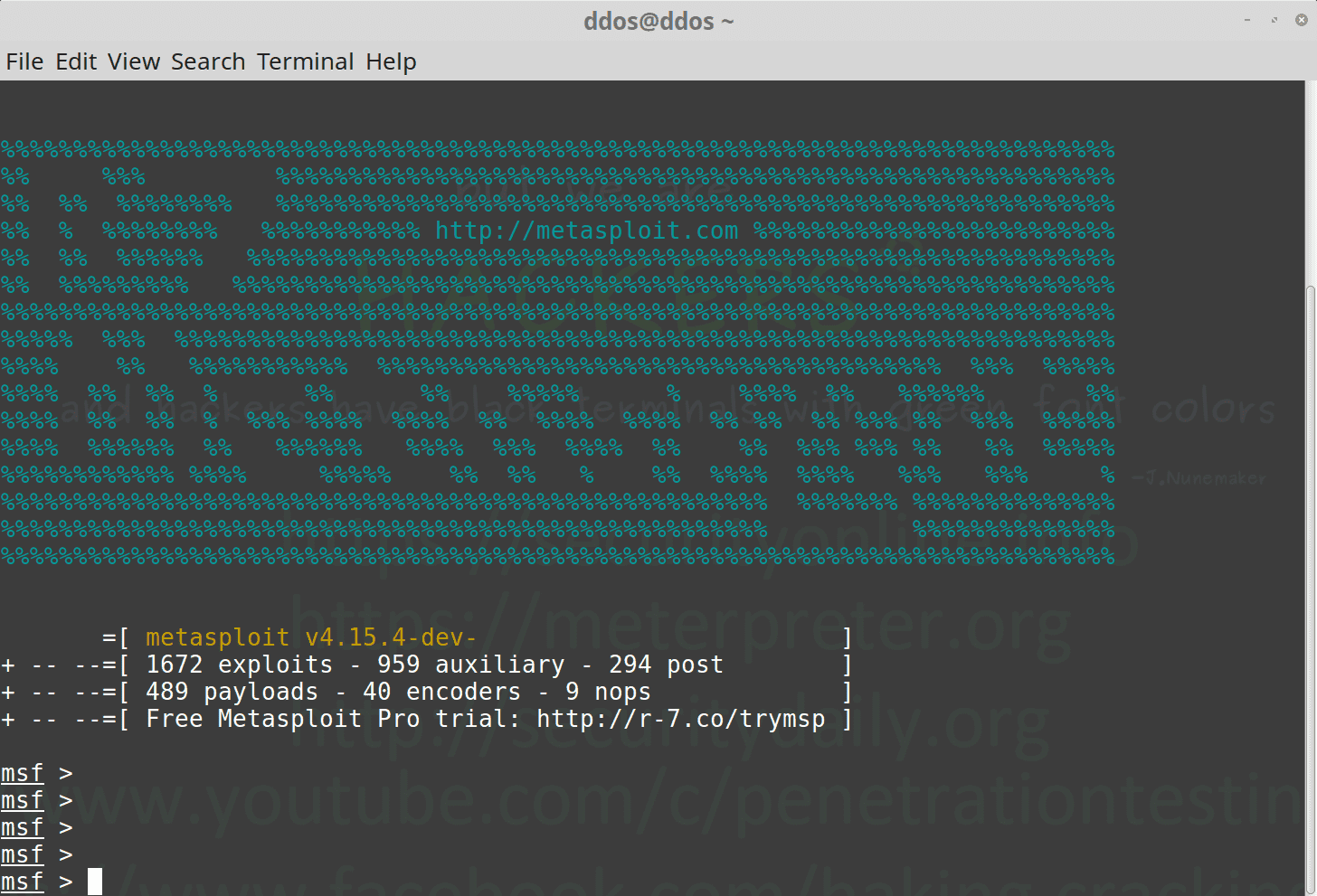


How To Install Metasploit Framework On Ubuntu Linux Mint Penetration Testing



How To Change File Permissions In Linux Skillsugar



Command Line Quick Tips Permissions Fedora Magazine


Linux Commands Linuxconfig Org
/create-directories-linux-mkdir-command-3991847-55ea75a52f7842a2af0fdfe0b7470270.gif)


How To Create Directories In Linux With The Mkdir Command



Ubuntu Users How Do You Even Launch Qgc Using Qgroundcontrol Discussion Forum For Px4 Pixhawk Qgroundcontrol Mavsdk Mavlink



How To Execute A Run Or Bin File In Ubuntu How To Ubuntu



Install Sp Flash Tool On Ubuntu



Using Chmod Command Octal Youtube



Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu



What Is Tty Command In Linux Ubuntu With Examples



Chmod X Explained Everything You Need To Know



How To Execute Install Sh Files In Linux Using Terminal 9 Steps



Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Linux Line Tools Thing 1
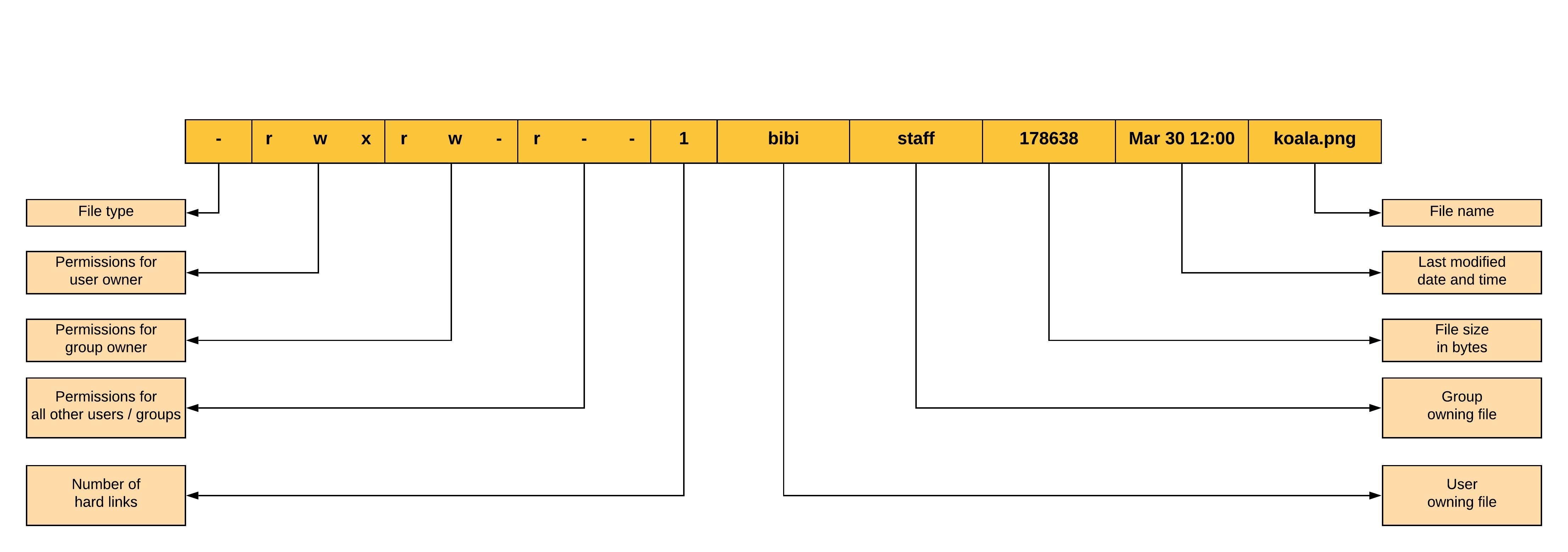


Linux File Permissions And Ownership By Udara Bibile Level Up Coding



Updating Spigot On Ubuntu Server With Multicraft It From Valdemar



The Chmod Command And Linux File Permissions Explained



Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex


35 Linux Basic Commands Every User Should Know Cheat Sheet
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)


How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux



Howto Find Keyword In Files With Grep In Ubuntu
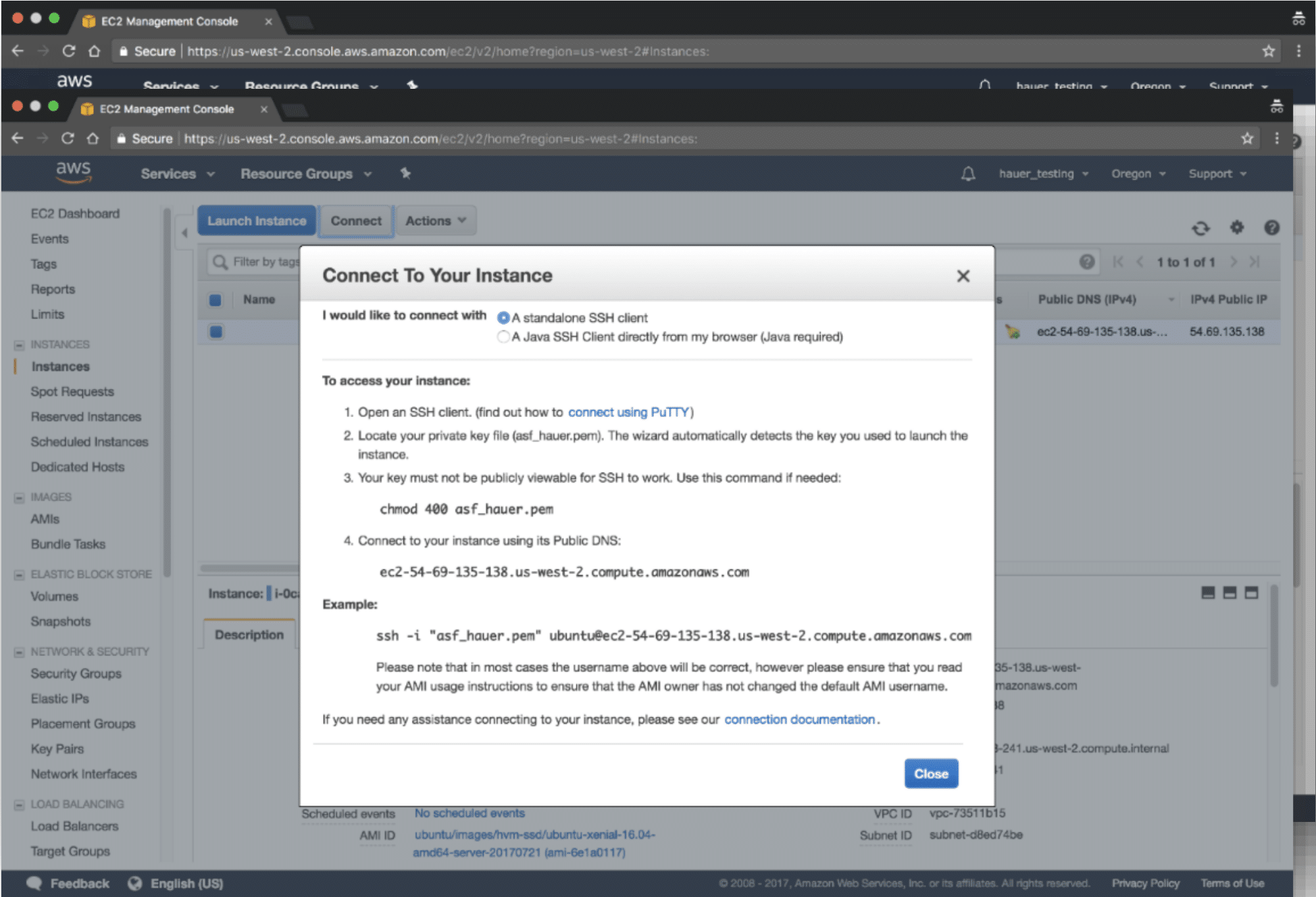


How To Connect To Ec2 With Ssh Mac Os X Asf


Set Permissions On Files Directories Using Chmod In Ubuntu Techpiezo



Error In Project Setup On Ubuntu Environment Stack Overflow



How To Install Dropbox On Ubuntu Linuxfordevices



Chmod Command In Ubuntu Youtube



Some Helpful Linux Commands Recently For A Coding Challenge I Was By Kate Schlunz Medium



How To Install Netbeans In Ubuntu Desktop



Bash Chmod U X Problem In Case Statement In Shell Script Ask Ubuntu
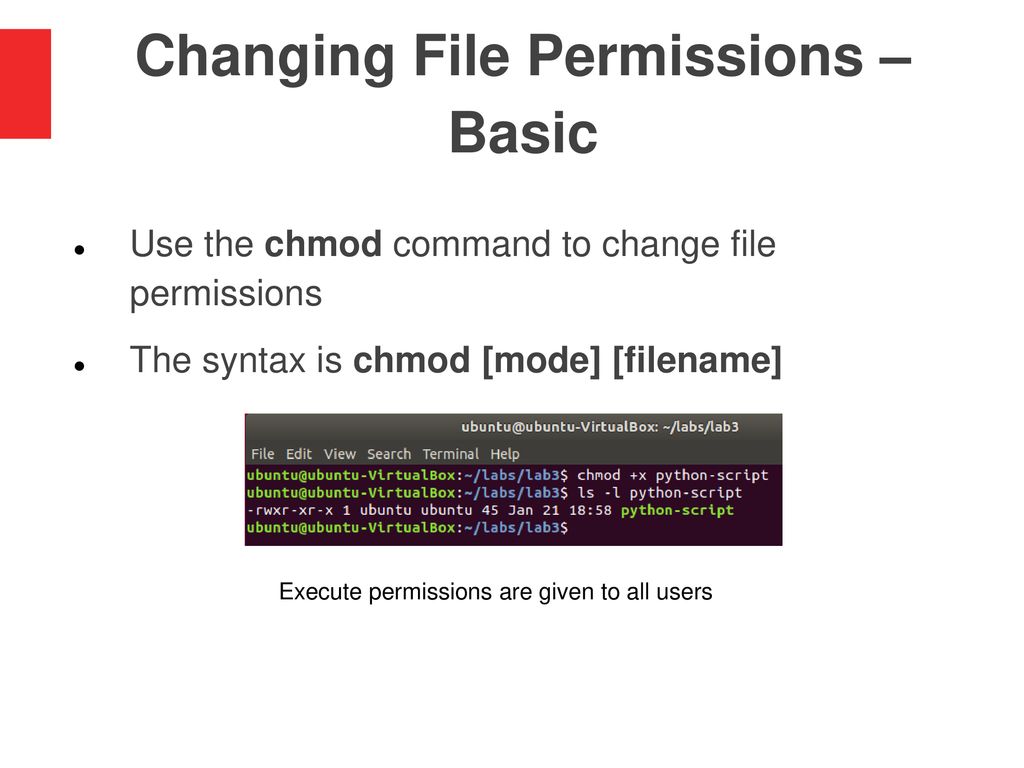


Lab 3 File Permissions Ppt Download



Ubuntu Common Commands Learn Computer Coding Linux Operating System Computer Coding



How To Install Midnight Commander In Linux Linuxhelp Tutorials



Linux Cheat Sheet Commands Pdf Download Printable


How To Change Welcome Message Motd On Ubuntu 18 04 Server Linuxconfig Org



Ubuntu Bash Tutorial Basic Utilities Sumguy S Ramblings


1



How To Write A Shell Script Using Bash Shell In Ubuntu 8 Steps



Chmod Command Explained Ubuntu In Virtual Box Windows 10 Youtube



How To Open Up Sh Extension In Ubuntu Stack Overflow


Willus Com S K2pdfopt Help Page



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿